Over the past several years, a number of misconceptions have emerged about how the search engines operate. For the beginner SEO, this causes confusion about what's required to perform effectively. In this section, we'll explain the real story behind the myths.
Search Engine Submission
In classical SEO times (the late 1990s), search engines had submission forms that were part of the optimization process. Webmasters and site owners would tag their sites and pages with keyword information, and submit them to the engines. Soon after submission, a bot would crawl and include those resources in their index. Simple SEO!
Unfortunately, this process didn't scale very well, the submissions were often spam, so the practice eventually gave way to purely crawl-based engines. Since 2001, not only has search engine submission not been required, but has become virtually useless. The engines all publicly note that they rarely use submitted URLs, and that the best practice is to earn links from other sites. This will expose your content to the engines naturally.
You can still sometimes find submission pages (here's one for Bing), but these are remnants of the past, and are unnecessary in the practice of modern SEO. If you hear a pitch from an SEO offering search engine submission services, run, don't walk, to a real SEO. Even if the engines used the submission service to crawl your site, you'd be unlikely to earn enough link juice to be included in their indices or rank competitively for search queries.

Meta Tags
Once upon a time, meta tags (in particular, the meta keywords tag) were an important part of the SEO process. You would include the keywords you wanted your site to rank for, and when users typed in those terms, your page could come up in a query. This process was quickly spammed to death, and was eventually dropped by all the major engines as an important ranking signal.
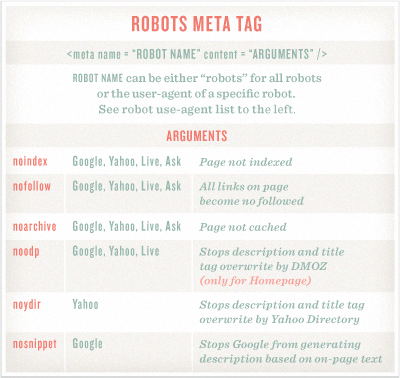
Other tags, in particular the title tag and meta description tag(covered previously in this guide), are crucial for quality SEO. Additionally, the meta robots tag is an important tool for controlling crawler access. So, while understanding the functions of meta tags is important, they're no longer the central focus of SEO.
Keyword Stuffing
Ever see a page that just looks spammy? Perhaps something like:
"Bob's cheap Seattle plumber is the best cheap Seattle plumber for all your plumbing needs. Contact a cheap Seattle plumber before it's too late."
Not surprisingly, a persistent myth in SEO revolves around the concept that keyword density—the number of words on a page divided by the number of instances of a given keyword—is used by the search engines for relevancy and ranking calculations.
Despite being disproved time and again, this myth has legs. Many SEO tools still feed on the concept that keyword density is an important metric. It's not. Ignore it and use keywords intelligently and with usability in mind. The value from an extra 10 instances of your keyword on the page is far less than earning one good editorial link from a source that doesn't think you're a search spammer.
Paid Search Helps Bolster Organic Results
Put on your tin foil hats; it's time for the most common SEO conspiracy theory: spending on search engine advertising (pay per click, or PPC) improves your organic SEO rankings.
In our considerable experience and research, we've never seen evidence that paid advertising positively affects organic search results. Google, Bing, and Yahoo! have all erected walls in their organizations specifically to prevent this type of crossover.
At Google, advertisers spending tens of millions of dollars each month have noted that even they cannot get special access or consideration from the search quality or web spam teams. So long as the search engines maintain this separation, the notion that paid search bolsters organic results should remain a myth.
SEARCH ENGINE SPAM
As long as there is search, there will be spam. The practice of spamming the search engines—creating pages and schemes designed to artificially inflate rankings or abuse the ranking algorithms—has been rising since the mid-1990s.
The stakes are high. One SEO noted that a single day ranking atop Google's search results for the query "buy viagra" could bring upwards of $20,000 in affiliate revenue. So it's little wonder that manipulating the engines is such a popular activity. However, it has become increasingly difficult and, in our opinion, less and less worthwhile for two reasons:
1. Not Worth the Effort
Users hate spam, and the search engines have a financial incentive to fight it. Many believe that Google's greatest product advantage over the last 10 years has been its ability to control and remove spam better than its competitors. It's undoubtedly something all the engines spend a great deal of time, effort, and resources on. While spam still works on occasion, it generally takes more effort to succeed than producing good content, and the long-term payoff is virtually non-existent.
Instead of putting all that time and effort into something that the engines will throw away, why not invest in a value-added, long-term strategy instead?
2. Smarter Engines
Search engines have done a remarkable job identifying scalable, intelligent methodologies for fighting spam manipulation, making it dramatically more difficult to adversely affect their intended algorithms. Metrics like Moz's TrustRank, statistical analysis, and historical data, have all driven down the value of search spam and made white hat SEO tactics (those that don't violate the search engines' guidelines) far more attractive.
More recently, Google's Panda update introduced sophisticated machine learning algorithms to combat spam and other low-value pages, and the search engines continue to innovate and raise the bar for delivering quality results.
We obviously don't recommend employing spam tactics. But to assist the large number of SEOs who seek help when their sites get penalized, banned, or flagged, it is worthwhile to review some of the factors the engines use to identify spam. For additional details about spam from the engines, see Google's Webmaster Guidelinesand Bing's Webmaster FAQs (PDF).
The important thing to remember is this: manipulative techniques generally won't help you, and they often result in search engines imposing penalties on your site.
| ||
PAGE-LEVEL SPAM ANALYSIS
Keyword Stuffing
One of the most obvious and unfortunate spamming techniques, keyword stuffing, involves littering keyword terms or phrases repetitively on a page in order to make it appear more relevant to the search engines. As discussed above, this strategy is almost certainly ineffectual.
Scanning a page for stuffed keywords is not terribly challenging, and the engines' algorithms are all up to the task. You can read more about this practice, and Google's views on the subject, in a blog post from the head of their web spam team: SEO Tip: Avoid Keyword Stuffing.

Manipulative Linking
One of the most popular forms of web spam, manipulative link acquisition, attempts to exploit the search engines' use of link popularity in their ranking algorithms to artificially improve visibility. This is one of the most difficult forms of spamming for the search engines to overcome because it can come in so many forms. A few of the many ways manipulative links can appear include:
- Reciprocal link exchange programs: Sites create link pages that point back and forth to one another in an attempt to inflate link popularity. The engines are very good at spotting and devaluing these as they fit a very particular pattern.
- Link schemes: These include "link farms" and "link networks" where fake or low-value websites are built or maintained purely as link sources to artificially inflate popularity. The engines combat these by detecting connections between site registrations, link overlap, and other methods targeted at common link scheme tactics.
- Paid links: Those seeking to earn higher rankings buy links from sites and pages willing to place a link in exchange for money. These sometimes evolve into larger networks of link buyers and sellers, and although the engines work hard to stop them (Google in particular has taken dramatic actions), they persist in providing value to many buyers and sellers (more on that perspective).
- Low quality directory links: These are a frequent source of manipulation for many in the SEO field. A large number of pay-for-placement web directories exist to serve this market and pass themselves off as legitimate, with varying degrees of success. Google often takes action against these sites by removing the PageRank score from the toolbar (or reducing it dramatically), but won't do this in all cases.
There are many more manipulative link building tactics that the search engines have identified. In most cases, they have found algorithmic methods for reducing their impact. As new spam systems emerge, engineers will continue to fight them with targeted algorithms, human reviews, and the collection of spam reports from webmasters and SEOs.
Cloaking
A basic tenet of search engine guidelines is to show the same content to the engine's crawlers that you'd show to a human visitor. This means, among other things, not to hide text in the HTML code of your website that a normal visitor can't see.
When this guideline is broken, the engines call it "cloaking" and take action to prevent these pages from ranking in their results. Cloaking can be accomplished in any number of ways and for a variety of reasons, both positive and negative. In some cases, the engines may let practices that are technically cloaking pass because they contribute to a positive user experience. For more on the subject of cloaking and the levels of risk associated with various tactics, see our article on White Hat Cloaking.
Low Value Pages
Although it may not technically be considered web spam, the engines all have methods to determine if a page provides unique content and value to its searchers. The most commonly filtered types of pages are thin affiliate content, duplicate content, and dynamically-generated content pages that provide very little unique text or value. The engines are against including these pages and use a variety of content and link analysis algorithms to screen out low value pages.
Google's 2011 Panda update took aggressive steps to reduce low quality content across the web, and Google continues to iterate on this process.
DOMAIN LEVEL SPAM ANALYSIS
In addition to scanning individual pages for spam, engines can also identify traits and properties across entire root domains or subdomains that could flag them as spam.
Linking Practices
Just as with individual pages, the engines can monitor the kinds of links and quality of referrals sent to a website. Sites that are clearly engaging in the manipulative activities described above on a consistent or seriously impacting way may see their search traffic suffer, or even have their sites banned from the index. You can read about some examples of this from past posts, including Widgetbait Gone Wild and the more recent coverage of theJC Penney Google penalty.

Trustworthiness
Websites that have earned trusted status are often treated differently from those that have not. SEOs have commented on the double standards that exist for judging big brand, high-importance sites compared to newer, independent sites. For the search engines, trust most likely has to do with the links your domain has earned. If you publish low-quality, duplicate content on your personal blog, then buy several links from spammy directories, you're likely to encounter considerable ranking problems. However, if you post that same content on Wikipedia, even with the same spammy links pointing to the URL, it would likely still rank tremendously well. Such is the power of domain trust and authority.
Trust can also be established through inbound links. A little duplicate content and a few suspicious links are far more likely to be overlooked if your site has earned hundreds of links from high-quality, editorial sources like CNN.com or Cornell.edu.
Content Value
As we've seen, an individual page's value is computed in part based on its uniqueness and the visitor's experience; likewise is the entire domain's value assessed. Sites that primarily serve non-unique, non-valuable content may find themselves unable to rank, even if classic on- and off-page SEO is well-optimized. The engines simply don't want thousands of copies of Wikipedia filling up their indexes, so they use algorithmic and manual review methods to prevent this.
Search engines constantly evaluate the effectiveness of their own results. They measure when users click on a result, quickly hit the back button on their browser, and try another result. This indicates that the result they served didn't meet the user's expectations.
It's not enough just to rank for a query. Once you've earned your ranking, you have to prove it over and over again.
So How Do You Know If You’ve Been Bad?
It can be tough to know if your site or page actually has a penalty. Sometimes, search engines' algorithms change. Or maybe you changed something on your site that negatively impacted your rankings. Before you assume you've been penalized, check for the following:

Once you’ve ruled out the list below, follow the flowchart beneath for more specific advice.
Errors
Errors on your site that may have inhibited or prevented crawling. Google's Webmaster Toolsis a good, free place to start.
Changes
Changes to your site or pages that may have changed the way search engines view your content. (on-page changes, internal link structure changes, content moves, etc.).
Similarity
Check for sites that share similar backlink profiles, and see if they’ve also lost rankings. When the engines update ranking algorithms, link valuation and importance can shift, causing ranking movements.
Duplicate Content
Modern websites are rife with duplicate content problems, especially when they scale to large size. Check out this post on duplicate content to identify common problems.

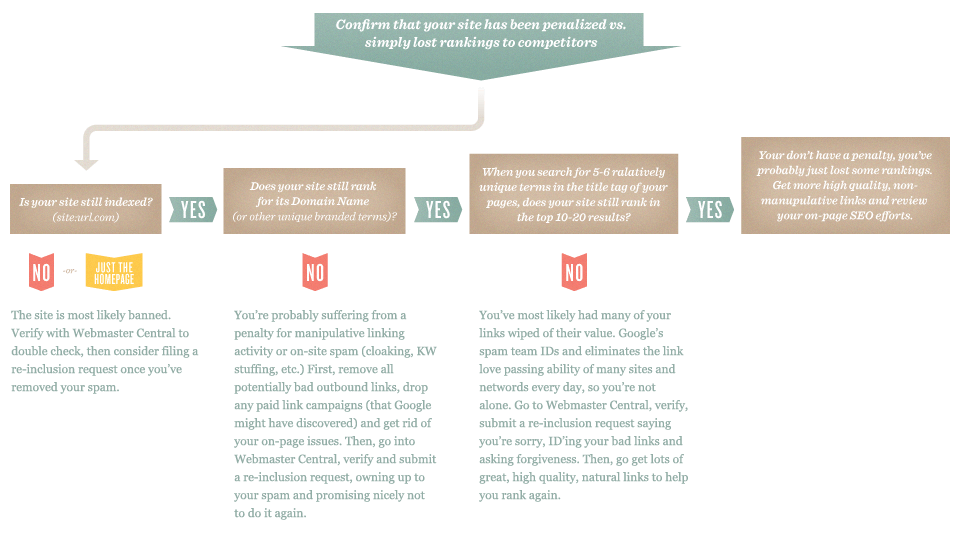
While this chart’s process won’t work for every situation, the logic has proven reliable in helping us identify spam penalties and mistaken flagging for spam by the engines, and separating those from basic ranking drops. This page from Google (and the embedded YouTube video) may also provide value on this topic.
Getting Penalties Lifted
The task of requesting reconsideration or re-inclusion in the engines is painful and often unsuccessful. It's also rarely accompanied by any feedback to let you know what happened or why. However, it is important to know what to do in the event of a penalty or banning.
- If you haven't already, register your site with the engine's Webmaster Tools service (Google's and Bing's). This registration creates an additional layer of trust and connection between your site and the search engine teams.
- Make sure to thoroughly review the data in your Webmaster Tools accounts, from broken pages to server or crawl errors to warnings or spam alert messages. Very often, what's initially perceived as a mistaken spam penalty is, in fact, related to accessibility issues.
- Send your reconsideration/re-inclusion request through the engine's Webmaster Tools service rather than the public form; again, this creates a greater trust layer and a better chance of hearing back.
- Full disclosure is critical to getting consideration. If you've been spamming, own up to everything you've done—links you've acquired, how you got them, who sold them to you, etc. The engines, particularly Google, want the details so they can improve their algorithms. Hold back, and they're likely to view you as dishonest, corrupt, or simply incorrigible (and they probably won't respond).
- Remove or fix everything you can. If you've acquired bad links, try to get them taken down. If you've done any manipulation on your own site (over-optimized internal linking, keyword stuffing, etc.), get it off before you submit your request.
- Get ready to wait. Responses can take weeks, even months, and re-inclusion itself, if it happens, is a lengthy process. Hundreds, perhaps thousands, of sites are penalized every week; you can imagine the request backlog.
- If you run a large, powerful brand on the web, re-inclusion can be faster by going directly to an individual source at a conference or event. Engineers from all of the engines regularly participate in search industry conferences (SMX, SES, Pubcon, etc.). The value of quickly being re-included can be worth the price of admission.
Be aware that with the search engines, lifting a penalty is not their obligation or responsibility. Legally, they have the right to include or reject any site or page. Inclusion is a privilege, not a right; be cautious and don't apply SEO techniques that you're skeptical about, or you might find yourself
Source: Moz
Author: Bryan Granse
Contact: Click Me